JavaScript provides some optional attributes that enhance the functionality of cookies. Here, is the list of some attributes with their description.
| Attributes | Description |
|---|---|
| expires | It maintains the state of a cookie up to the specified date and time. |
| max-age | It maintains the state of a cookie up to the specified time. Here, time is given in seconds. |
| path | It expands the scope of the cookie to all the pages of a website. |
| domain | It is used to specify the domain for which the cookie is valid. |
Cookie expires attribute
The cookie expires attribute provides one of the ways to create a persistent cookie. Here, a date and time are declared that represents the active period of a cookie. Once the declared time is passed, a cookie is deleted automatically.
Let's see an example of cookie expires attribute.
Cookie max-age attribute
The cookie max-age attribute provides another way to create a persistent cookie.
Here, time is declared in seconds. A cookie is valid up to the declared time only.
Let's see an example of cookie max-age attribute.
Cookie path attribute
If a cookie is created for a webpage, by default, it is valid only for the current directory and sub-directory. JavaScript provides a path attribute to expand the scope of cookie up to all the pages of a website.
Cookie path attribute Example
Let's understand the path attribute with the help of an example.
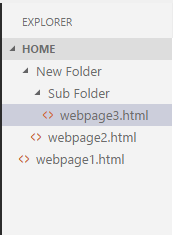
Here, if we create a cookie for webpage2.html, it is valid only for itself and its sub-directory (i.e., webpage3.html). It is not valid for webpage1.html file.
In this example, we use path attribute to enhance the visibility of cookies up to all the pages.
Here, you all just need to do is to maintain the above directory structure and put the below program in all three web pages. Now, the cookie is valid for each web page.
Cookie domain attribute
A JavaScript domain attribute specifies the domain for which the cookie is valid. Let's suppose if we provide any domain name to the attribute such like:
Here, the cookie is valid for the given domain and all its sub-domains.
However, if we provide any sub-domain to the attribute such like:
Here, the cookie is valid only for the given sub-domain. So, it's a better approach to provide domain name instead of sub-domain.
No comments:
Post a Comment