JavaScript is a prototype-based language that facilitates the objects to acquire properties and features from one another. Here, each object contains a prototype object.
In JavaScript, whenever a function is created the prototype property is added to that function automatically. This property is a prototype object that holds a constructor property.
Syntax:
What is the requirement of a prototype object?
Whenever an object is created in JavaScript, its corresponding functions are loaded into memory. So, a new copy of the function is created on each object creation.
In a prototype-based approach, all the objects share the same function. This ignores the requirement of creating a new copy of function for each object. Thus, the functions are loaded once into the memory.
Prototype Chaining
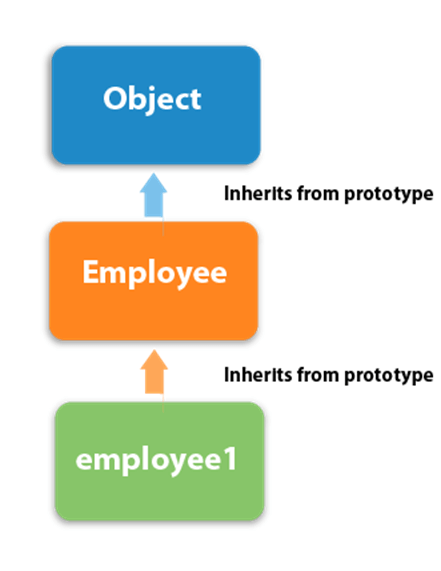
In JavaScript, each object contains a prototype object that acquires properties and methods from it. Again an object's prototype object may contain a prototype object that also acquires properties and methods, and so on. It can be seen as prototype chaining.
JavaScript Prototype Object Example 1
Let's see an example to add a new method to the constructor function.
Output:
Santosh Singh Vina Devi
Example 2
Let's see an example to add a new property to the constructor function.
Output:
Santosh Singh JavaScriptCodeGuruJi Vina Devi JavaScriptCodeGuruJi
Prototype Inheritance
All JavaScript objects inherit properties and methods from a prototype:
Dateobjects inherit fromDate.prototypeArrayobjects inherit fromArray.prototypePersonobjects inherit fromPerson.prototype
The
Object.prototype is on the top of the prototype inheritance chain:Date objects, Array objects, and Person objects inherit from Object.prototype.Adding Properties and Methods to Objects
Sometimes you want to add new properties (or methods) to all existing objects of a given type.
Sometimes you want to add new properties (or methods) to an object constructor.
Using the prototype Property
The JavaScript
prototype property allows you to add new properties to object constructors:Example
function Person(first, last, age, eyecolor) {
this.firstName = first;
this.lastName = last;
this.age = age;
this.eyeColor = eyecolor;
}
Person.prototype.nationality = "English";
The JavaScript
prototype property also allows you to add new methods to objects constructors:Example
function Person(first, last, age, eyecolor) {
this.firstName = first;
this.lastName = last;
this.age = age;
this.eyeColor = eyecolor;
}
Person.prototype.name = function() {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
};
No comments:
Post a Comment